Have you noticed how smart pet feeder manufacturing has transformed from a niche gadget industry into a critical part of modern pet brand strategies? Features like app control, built-in cameras, multi-pet feeding, and high-capacity designs are no longer optional—they’re the baseline customers expect. Yet for many brand owners, turning these expectations into reality can feel like navigating a maze of technical challenges and costly pitfalls.
Delays in product launches, inconsistent performance, escalating after-sales support, and OEM partnerships that seem promising on paper—but stumble in real life—are more common than most admit.
Often, the problem isn’t the market itself. Instead, it’s decisions made during manufacturing judgment errors—from late-stage design choices to incomplete technical insights, or simply chasing short-term cost savings at the expense of long-term reliability.
For brand owners who want to go beyond treating production as a transactional task, this guide positions smart pet feeder manufacturing as a strategic advantage. You might find insights on leading OEM solutions, cost frameworks, and factory capabilities especially helpful when planning your next product launch.
By understanding these factors early, you can avoid common pitfalls, improve product quality, and accelerate time-to-market—all while safeguarding your brand reputation.
Smart Pet Feeder Manufacturing Today: What Brand Owners Often Overlook
Many brands enter the smart feeder market assuming that once a prototype works, mass production will naturally follow. The reality is very different.
Smart pet feeder manufacturing is a multi-layered challenge, blending mechanical engineering, electronics, firmware, and long-term reliability considerations. Each layer must work together seamlessly to avoid costly setbacks.
Why “Working Samples” Don’t Guarantee Mass Production Success
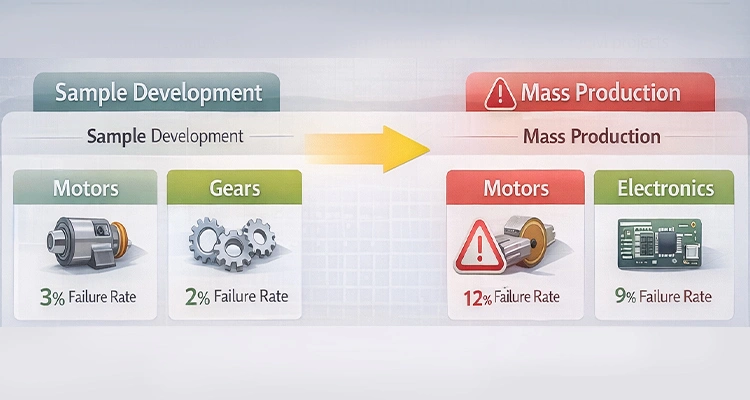
A working sample only demonstrates that a product can function once—it does not guarantee consistent performance at scale. This distinction is especially critical when smart pet feeder electronics design is simplified or rushed during the prototype phase.
Subtle issues with PCB stability, power management, or firmware edge cases often appear only after hundreds or thousands of units are produced.
Data from OEM projects shows that around 20% of new feeders encounter firmware or electronics issues within the first 1,000 units. Among these, 8% require rework, 5% generate warranty claims, and total cost overruns can reach 12–18% of the project budget. These numbers illustrate the gap between sample success and scalable manufacturing.
For camera-enabled feeders, you might find camera-enabled feeder engineering insights helpful. They highlight how early engineering decisions directly affect long-term reliability and product consistency.
The Hidden Gap Between Product Concept and Scalable Manufacturing
The most overlooked gap appears between industrial design approval and engineering validation. Many projects underestimate:
- Structural stress during extended use
- Real-world feeding behavior variations
- Motor wear under uneven food loads
Without early checks such as pet feeder PCB layout optimization or mechanical tolerance analysis, brands often face recalls, warranty claims, or reputational damage later in the process.
Smart Pet Feeder Manufacturing Process: From Concept to Mass Production
Successfully bringing a smart feeder to market requires a disciplined, step-by-step approach. Shortcuts may seem tempting but can cost significantly in the long run.
Early-Stage Risks in Smart Pet Feeder Manufacturing Projects
The most critical decisions occur before tooling begins. Many OEM projects fail quietly at this stage, often due to underestimated engineering challenges or incomplete technical specifications.
Product Structure Validation vs Visual Design Approval
Visual approval alone doesn’t guarantee structural safety. Feed paths, bowl alignment, anti-jam mechanisms, and cleaning accessibility must all be tested under repeated use.
This is particularly vital for wet food automatic feeder manufacturing, where moisture and residue complicate mechanical reliability. For practical OEM strategies, wet food feeder OEM practices provides hands-on guidance for addressing these challenges.
Electronics and Firmware Development Risks
Electronics failure rarely stems from a single component. Instead, it’s a system-level balance issue. Poor power regulation, signal noise, or firmware oversights can destabilize Wi-Fi modules and cameras, particularly in smart pet feeder with camera manufacturing projects.
Connected feeders face additional challenges in multi-pet households, making early integration and testing essential.
Prototype Testing, Pilot Run, and Consistency Challenges
Skipping structured sample development for smart pet feeders often results in unpleasant surprises during scale-up.
A disciplined prototype validation process, followed by a controlled pilot run in smart pet feeder manufacturing, allows brands to verify consistency, test smart feeder reliability, and identify potential issues before committing to mass production.
For step-by-step guidance, you might find the pet feeder sample evaluation guide helpful. It outlines practical strategies for testing prototypes, validating functionality, and ensuring your smart feeder performs reliably at scale.
Smart Pet Feeder OEM Solutions for Brand Owners
Navigating smart pet feeder manufacturing can feel like walking a tightrope. Done well, OEM partnerships accelerate product launches, improve quality, and open customization opportunities. Done poorly, they create delays, hidden costs, and frustration that every brand owner knows too well.
Customization Scope in OEM Smart Pet Feeder Manufacturing
True OEM solutions go far beyond simply adding a logo. They touch every aspect of design, engineering, and functionality. Key areas include:
- Structural adaptations for large-capacity pet feeder manufacturing to accommodate bigger breeds or multi-pet households
- Multi-channel dispensing logic for multi-pet dispensing systems, ensuring accurate portion control and consistent feeding
- Material upgrades such as stainless steel bowl pet feeder integration for durability and hygiene
Every customization decision influences tooling, yield rate, and long-term cost. For brands building advanced multi-pet setups, dual-pet feeder OEM design strategies offers valuable engineering guidance and practical factory insights.
Similarly, for premium materials like stainless steel, stainless bowl feeder OEM solutions explains trade-offs between quality, cost, and scalability.
MOQ, Lead Time, and Private Label Smart Pet Feeder Considerations
Decisions around MOQ, lead time, and private label options define the success of your smart pet feeder OEM project timeline. Lower MOQs may allow smaller batches but often increase per-unit cost or limit the depth of customization—trade-offs every brand owner must weigh carefully.
When OEM Accelerates Growth — and When It Slows You Down
OEM works best when factories are treated as early-stage engineering partners rather than last-minute executors. Engaging suppliers late in the process almost always results in rework, delays, and stress.
For real-world lessons drawn from factory-side engineering decisions, the large dog feeder case study by Petrust® offers a practical look into how manufacturing choices impact reliability at scale.
OEM vs ODM Smart Pet Feeder: Choosing the Right Manufacturing Model
The choice between OEM and ODM isn’t just a cost calculation—it’s a strategic brand decision.
OEM vs ODM Smart Pet Feeder: Cost, Control, and Risk Comparison
OEM gives brands greater control over design, firmware, and long-term upgrades—but requires deeper technical involvement. ODM can deliver faster market entry, yet limits differentiation and long-term flexibility.
Smart Pet Feeder ODM for Faster Market Entry
ODM solutions are useful for testing new markets or quickly expanding product lines. Still, brands often underestimate long-term dependency risks when relying solely on ODM partners.
Long-Term Brand Implications of Each Model
Brands planning multi-generation product lines need to align tooling ownership, firmware control, and upgrade paths with long-term goals.
For a global perspective on sourcing choices, China vs US smart feeder sourcing comparison offers practical benchmarks for cost, lead time, and compliance considerations.
Smart Pet Feeder Manufacturing Cost Breakdown (2026)
Cost transparency is where strong brands distinguish themselves from fragile ones. Understanding what drives pricing allows better planning, avoids surprises, and supports scalable growth.
Cost Drivers in Smart Pet Feeder Manufacturing
Key cost components include:
- Motor selection and performance for smart pet feeders
- Firmware complexity and integration
- Camera modules and sensor accuracy
- Assembly yield and quality consistency
Errors in torque calculation for pet feeder motors or gear system design for pet feeders are surprisingly common. Over-engineering often leads to premature failures, higher costs, and wasted production cycles.
How MOQ Affects Smart Pet Feeder Pricing
MOQ influences not only unit cost but also supplier commitment, QA depth, and production scheduling priority. Smaller batches may seem cheaper initially, but they can slow down quality inspections and affect reliability.
Injection Mold Cost for Smart Pet Feeders
Tooling is a capital investment with long-term implications. Upfront price matters less than ownership terms and the ability to reuse molds for future iterations.
For a deeper analysis, you might find this smart feeder OEM cost breakdown guide helpful—it provides practical insights into molding strategy, cost allocation, and ROI for your next product line.
Smart Pet Feeder OEM Pricing: What Low Quotes Often Hide
Low quotes in smart pet feeder manufacturing rarely tell the whole story. While a seemingly attractive price might grab your attention, hidden costs often emerge after tooling, QA, and production scale-up.
Many brand owners discover too late that initial savings can translate into higher warranty claims, delayed shipments, or costly firmware fixes. You might find detailed OEM pricing insights for smart feeders helpful in planning realistic budgets and avoiding unpleasant surprises.
Common Cost Traps in Smart Pet Feeder Manufacturing Projects
Some of the most frequent pitfalls include:
- Underestimated QA labor during pilot and mass production
- Simplified testing protocols that skip stress and endurance cycles
- Material substitutions made after sample approval
These “shortcuts” can significantly affect product reliability, and understanding them early is crucial for maintaining both cost efficiency and brand trust.
For context on market-driven engineering challenges, research published in Engineering Proceedings demonstrates how integrating IoT and sensor fusion into smart feeders enhances precision and pet health outcomes.
Tooling Ownership and Long-Term Production Cost Risks
Unclear tooling ownership can lock a brand into a single supplier indefinitely, limiting flexibility in future product updates or expansions. Ensuring that your smart pet feeder manufacturing contracts clearly define tooling rights can protect both margins and strategic freedom.
Quality Shortcuts that Increase After-Sales Costs
Skipping endurance or stress testing often leads to motor failures, feeding inaccuracies, and warranty claims months after launch.
For context on market-driven engineering challenges, research published in Engineering Proceedings demonstrates how integrating IoT and sensor fusion into smart feeders enhances precision and pet health outcomes — underscoring why comprehensive engineering investment is critical.
How to Choose a Smart Pet Feeder Manufacturing Factory
Selecting a factory goes beyond size or headline production capacity. It’s about system capability, engineering depth, and process reliability.
Smart Pet Feeder Factory Audit Checklist
A thorough factory audit should include:
- Engineering depth and innovation capability
- Firmware ownership and update control
- Change management process for design revisions
- Traceability systems for both components and final assemblies
These measures are critical when learning how to evaluate pet feeder manufacturers properly. For compliance verification and structured audit guidance, you can find certified pet feeder factory checklist helpful in ensuring every aspect of the production process meets international standards.
In-House vs Outsourced Electronics Manufacturing
Factories with in-house electronics lines reduce coordination risks, accelerate firmware iteration, and allow faster problem resolution. This capability often separates reliable smart pet feeder manufacturing in China from less capable OEM partners.
Production Capacity & Lead Time Considerations
Capacity must match your growth trajectory—not just first orders. Evaluating pet feeder OEM factory China partners should include projections for scaling, bottleneck mitigation, and flexible production scheduling to avoid missed market windows.
Quality Control & Certification in Smart Pet Feeder Production
Quality control is not a single checkpoint—it’s a system embedded throughout the manufacturing process.
Smart Pet Feeder Quality Control vs Final Inspection
Final inspection only catches visible defects. A robust process-oriented QC system prevents defects before they occur, from firmware testing to mechanical endurance.
According to the Consumer IoT Device Cybersecurity Standards 2025 report, IoT devices like smart feeders should adopt harmonized cybersecurity frameworks to protect consumer safety and data integrity.
CE, FCC, RoHS Smart Pet Feeder Compliance
Certification readiness must be built into both hardware and firmware from day one.
Research by the Open Connectivity Foundation (OCF) highlights interoperability and certification frameworks essential for IoT devices, reinforcing why smart pet feeders designed for global markets must integrate industry-wide connectivity standards.
Firmware Stability & Electronics QC Requirements
Long-term reliability relies on stable power, OTA safeguards, and fail-safe logic. Implementing an IoT Trust Framework® for device security can significantly enhance firmware stability, data protection, and consumer confidence in connected smart feeders.
Common Manufacturing Defects in Smart Pet Feeders — and How to Prevent Them
Most defects are predictable—and preventable—if addressed during the design and pilot phases. Real-world usage often reveals feeding patterns and load conditions that lab tests alone cannot catch.
For more technical insight, you might find large-capacity smart pet feeder design insights helpful in understanding scaling issues and defect prevention strategies.
Why Smart Pet Feeder Manufacturing Defects Often Appear After Launch
Unexpected wear, motor strain, and firmware glitches usually surface only when feeders are in the hands of real users. Observing early adopters and structured pilot testing can highlight potential problem areas before full-scale production.
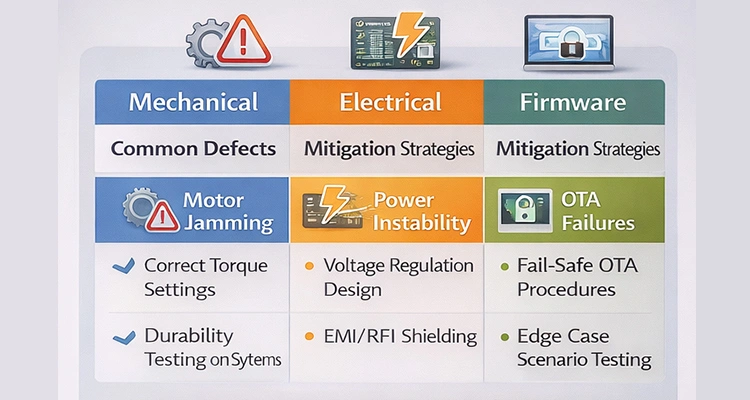
Mechanical Wear and Motor Torque Miscalculation
Underestimating mechanical wear or miscalculating motor torque can result in jamming, noise complaints, or uneven portioning. Proper simulation and stress testing help mitigate these risks.
Electronics Failure Caused by Unstable Power Design
Voltage fluctuations, poor regulation, or insufficient battery protection are top contributors to early electronics failures. Incorporating robust power design and monitoring during smart pet feeder manufacturing protects both your product and brand reputation.
Smart Pet Feeder Manufacturing Trends Brand Owners Should Watch in 2026
Staying on top of trends is useful only when they translate into actionable decisions.
Smart Pet Feeder Technology Trends Shaping OEM Decisions
AI feeding algorithms and adaptive scheduling are gaining traction but introduce higher firmware complexity.
Connectivity increases user value but also raises support responsibilities. IoT-enabled pet feeders demand careful firmware testing and security compliance to maintain trust.
2026 Materials & Sensor Trends
- Eco-friendly plastics and antimicrobial coatings are becoming standard for safe and durable feeders.
- High-precision load sensors and portion-detection cameras improve accuracy in dual- and multi-pet dispensing systems.
- Battery efficiency and power management improvements reduce warranty claims and long-term failures.
Practical Tip: Evaluating whether to invest early in AI scheduling or multi-camera modules can help brands avoid cost spikes later. These decisions directly impact tooling, PCB complexity, and assembly yield. According to the EN 17927 Security Evaluation Standard for IoT Platforms, holistic security evaluations strengthen compliance and build consumer trust.
Brand Failures & Lessons Learned
Case A
In one dual-pet feeder OEM China project, the timeline was pushed too aggressively. On paper, the product passed basic functional checks, but the portion logic hadn’t been fully stress-tested in real multi-pet scenarios.
Within the first month after launch, around 15% of units began showing feeding inconsistencies—an issue that quickly translated into customer complaints and returns. What looked like a small software shortcut early on ended up becoming a costly post-launch lesson.
Case B
Another project chose to outsource electronics development to move faster. While the initial prototype performed well, deeper firmware integration issues surfaced during scaled production.
Roughly 12% of units required a firmware rollback after shipment, forcing the team to pause and rerun the pilot phase. The delay wasn’t just about time—it disrupted the launch schedule and added unexpected coordination and validation costs.
Lessons Learned
Looking at these two cases, one thing becomes clear: problems rarely come from the market itself. They come from decisions made too late. Early engineering validation, well-structured pilot runs, and careful multi-pet dispensing calibration are what protect brands from expensive setbacks—and from losing hard-earned trust in the global market.
Final Thoughts – Turning Smart Pet Feeder Manufacturing into a Long-Term Competitive Advantage
Smart pet feeder manufacturing is much more than a production task—it’s a chance to turn your brand into a trusted leader. Every decision, from sourcing components to final QC, shapes not only the product but also your long-term reputation.
Brands that truly grasp how to source smart pet feeders, anticipate smart pet feeder OEM risks, and avoid common mistakes in pet feeder OEM projects are the ones whose products endure, delight customers, and create loyalty well beyond a single launch.
Selecting the right smart pet feeder supplier for brands isn’t just about getting the lowest price—it’s about securing long-term reliability, consistent quality, and a partner who can grow with your vision. Thoughtful collaboration at the start sets the stage for scalable production, smoother product iterations, and faster time-to-market.
Practical ways to start building this advantage include:
- Schedule a free 30-minute consultation to evaluate your feeder concept. Discuss your ideas with experts who understand both engineering realities and market expectations.
- You can request a sample audit report to understand potential OEM pitfalls. Reviewing real production examples can highlight hidden risks before they impact timelines or costs.
Taking these proactive steps ensures your smart pet feeder OEM project begins on solid footing, helping you avoid costly early-stage mistakes and creating a foundation for long-term competitive advantage.
Over time, these small but strategic choices compound into products that not only perform but also strengthen your brand in a crowded market.
FAQ: Quick Reference for Brand Owners
1. How can you verify smart feeder firmware stability before scaling to mass production?
Conducting structured pilot runs, testing edge cases, and simulating OTA updates are essential steps. You might find reviewing smart pet feeder product iteration insights helpful when designing your test protocols.
2. Which certifications are most critical when shipping globally?
CE, FCC, and RoHS provide the baseline for international markets. Depending on your target region, additional certifications may be required to ensure compliance and smooth customs clearance.
3. How do you avoid low-quote traps in OEM negotiations?
Beyond the unit price, evaluate tooling ownership, QA processes, and material substitutions. Paying attention to these factors can prevent hidden costs from eroding your margins.
4. How can you assess a factory’s engineering capability?
Look for in-house electronics production, firmware ownership, and a structured change management system. These indicators often differentiate reliable smart pet feeder manufacturing partners from those with inconsistent delivery.
5. What metrics indicate consistent production quality?
Monitor defect rates during pilot runs, assembly yield rates, and component variation across batch sizes. You can use a connected feeder factory audit checklist as a reference framework for internal reviews.
Author context: This guide is informed by factory-level OEM experience in smart pet feeder manufacturing, including multi-generation feeder development and large-scale production projects.